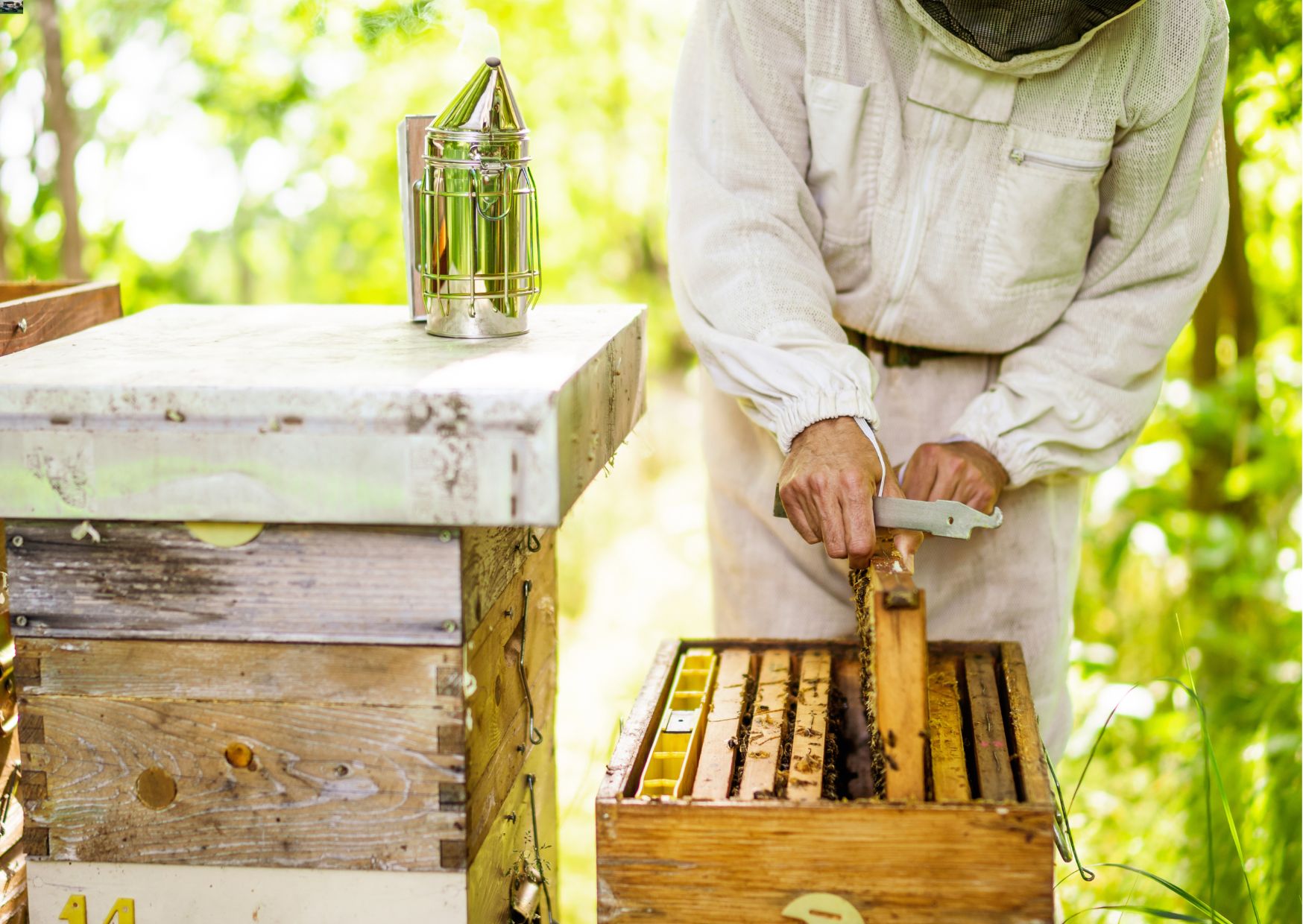
To become a beekeeper can be a fulfilling vocation or pastime in which one takes responsibility for bee colonies and extracts hive products such as honey and beeswax; beekeeping provides a valuable service to agriculture and the environment by supporting pollination and maintaining healthy bees.
What Are the Main Types of Beekeepers?
Role and Key Responsibilities
Hobbyist Beekeepers: Typically, hobby beekeepers rear a few hives as a pastime, with honey production being secondary to the pursuit of knowledge and stewardship of the local biotic environment.
Commercial Beekeepers: In contrast, commercial beekeepers often manage thousands of hives to produce honey, beeswax, and other products, or they provide pollination services to farmers.
Urban Beekeepers: Urban beekeepers keep hives in the city so the bees can help with the process of pollination and transmit awareness of the significance of bees to the community.
Organic Beekeepers: Organic beekeepers naturally manage their hives to produce organic honey for the market (it is not artificially altered, and no synthetic chemicals or antibiotics are used).
What Does a Beekeeper Do?
Managing Bee Colonies and Hives
To become a beekeeper, you inspect and manage hives, ensuring that colonies are healthy and productive.
Monitoring Bee Health and Behavior
They also watch the bees for disease, pests and other nuisances.
Harvesting Honey and Other Hive Products
To become a beekeeper, you harvest honey, beeswax, and other products, ensuring they are collected and processed properly.
Maintaining Hive Equipment
They maintain and repair hive equipment, ensuring that hives are safe and functional.
Preventing and Managing Pests and Diseases
To become a beekeeper, you use different methods to prevent and prepare for issues with pests or pathogens that could affect the bees.
Educating the Public About Bees and Beekeeping
They frequently have outreach projects aimed at educating the masses about the value of bees and about the need for beekeeping to be sustainable.

Average Beekeeper Salary
Salary Ranges Based on Experience and Location
Salaries vary greatly by experience, region and scale of the operation, but the average hobbyist beekeeper does not make a salary, while commercial beekeeper earnings in the UK range from £20,000-£40,000 annually and in the US from $25,000- $60,000.
Comparison of Incomes in Different Regions and Types of Beekeeping
This is reflected in large differences in incomes, depending on the location and the type of beekeeping. Higher-income can be expected from areas with high demand for beeswax products and pollination services.
Factors Influencing Beekeeper Salaries
Several factors can influence beekeeper salaries:
- Experience: the more experience beekeepers have, the more income they typically earn because beekeeping is a skill that grows with experience.
- The scale of Operations: Larger operations with more hives and more commercial activities tend to earn more money.
- Location: The spatial area where you operate has a significant influence on your income, considering that regions with higher demand for bee products and services are associated with higher earnings.
Beekeeper Skills
Technical Skills
- Knowledge of Bee Biology and Behavior: Understanding bee biology and behavior is essential for effective hive management and disease prevention.
- Hive Management Techniques: Proficiency in hive management techniques ensures healthy and productive colonies.
Soft Skills
- Attention to Detail: Attention to detail is necessary for monitoring bee health and identifying potential issues.
- Patience: Patience is crucial for working with bees and managing hives effectively.
- Problem-Solving: Effective problem-solving skills help beekeepers address challenges and maintain healthy colonies.
- Physical Stamina: Physical stamina is required for managing hives, lifting equipment, and working outdoors.

Beekeeper Tips
Staying Updated with Advancements in Beekeeping Techniques and Research: Make the effort to stay up to date on the newest beekeeping techniques and research.
Networking Via Beekeeping Associations and Clubs: Being a member of a beekeeping association and club offers networking opportunities as well as resources.
Experience Through Apprenticeships and Volunteering: Having practical experience through an apprenticeship or volunteer work is crucial for learning skills as well as building up your reputation.
Constant honing of their hive management skills: Regular practice and fine-tuning of their hive management skills allow beekeepers to have successful careers.
Beekeeper Requirements
Educational Requirements
- Basic Understanding of Biology and Ecology: Having a foundational knowledge of biology and ecology helps understand behaviour and proper hive management.
- Courses or Training Programs Relatable: Practical courses or a training program that’s relatable to the work is an important ally.
Certification Requirements
- Certification Through Beekeeping Associations: Certification by beekeeping associations signifies competence to the professional standards set by those bodies.
Experience Requirements
- Internships and volunteering: practical experience is essential for the development of your skills and reputation.
How to Become a Beekeeper
Completing Relevant Education
- Obtaining Basic Education in Biology or Agriculture: Several subjects in secondary school, especially biology, ecology and entomology, lay a good biological foundation for both biological control and ecological pest management.
- Take Beekeeping Courses or Workshops: Take up beekeeping courses or workshops to become properly trained in the use of the techniques and practices employed in this art/science.
Gaining Practical Experience
- Volunteer or Intern with Experienced Beekeepers: Gain practical experience by volunteering or interning with a skilled beekeeper to build up a portfolio of skills.
Obtaining Certification
- Beekeeping Association Certification: Gain certification as evidence that you can be trusted to keep bees at an acceptable standard.
Continuing Professional Development
- Workshops, Seminars, Webinars: Engage in continuous professional development through various training opportunities.
- Advanced Training and Specializations: Pursue advanced training and specialisations to further develop your expertise.
Networking
- Networking with Beekeeping Associations and Clubs: Join a beekeeping association and/or club to network with other individuals in your field and to stay abreast with trends, research and business ideas in the industry.
- Beekeeping Events and Conferences: Participate in as many beekeeping events and conferences as you can to network and learn from expert beekeepers.
Get Qualified as a Beekeeper
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Why should you become a Beekeeper?
To be able to pursue a profession that does all of the above and add highly esteemed beekeepers to the list of profiles is pretty awesome. So if you need further motivation to become a beekeeper, check out some of the reasons that are worth pursuing: You get to work with bees; Honey and other hive products are produced; Environmental sustainability is promoted; Respected career with high job satisfaction; Higher than average incomes are received; Personal fulfilment through meaningful career, making a significant impact on agriculture and the environment.
2. Is Beekeeping a Good Career Choice for You?
If you fancy nature, the outdoors, as well as bees and bee behaviours, then beekeeping is right up your alley. You’ll enjoy it if you’re meticulous, patient and a little physical, so long as you’re serious about environmental sustainability and love getting your hands dirty.
3. Beekeeper Salaries
Income levels for beekeepers vary by experience level, geography and scale of enterprise. To become a beekeeper operating as a recreational hobbyist pursuing beekeeping as a pastime may have no salary; a commercial beekeeper’s income ranges between £20,000 and £40,000 annually (depending on output) in the UK and $25,000 to $60,000 in the US due to the size of the operation, geographic location and the demand for bee products and pollination services.
4. Which Qualifications Can Help with a Career in Beekeeping?
It is necessary to study some general biology or agriculture, at least at the school level, or to attend special courses and training seminars in beekeeping. Joining professional organisations, for example, beekeeping associations will bring certification as a respected member, and the acquisition of adequate methods and competencies through practical experience with a master or mentor, including periods of internship or volunteering.
5. Do I Need to Be Experienced to Get Started?
No. Many people who are just learning how to beekeep take a Beginner’s Class or attend a workshop, work for a season with an experienced beekeeper, or even do a paid or volunteer internship. Being enthusiastic, eager to learn, and appreciating bees and other beings of the natural world are good starting points.
6. Beekeeper Career Outlook
The demand for bee products and pollination services is relatively steady, so the outlook for beekeeping as a career is quite favourable. People are better understanding the value of bees to agriculture and nature and, as long as this awareness is maintained, demand for beekeepers will remain steady or even increase. Job satisfaction is often very high for beekeepers. Earnings can be very good. And, because it’s a specialised and emerging profession, there are many opportunities for career advancement.
7. Beekeeper Hierarchy and Progressing Within the Role
The beekeeper career path is fairly simple and it looks like this. People normally start from low-level positions — they can be volunteers or apprentice beekeepers. With more experience and education one can move forward to middle-level positions — head beekeeper or apiary manager. Advanced-level positions include such as commercial beekeeper, beekeeping consultant or educator.
Continuing education and professional development help beekeepers increase their skills and raise their professional level, which helps to advance in their careers.
8. Beekeeper Exit Options and Opportunities
Except for the rare (usually very small-scale) full-time beekeeper, there are many alternatives to exiting their original vocation and career. Skills are gained that are readily transferrable – eg, into agriculture, environmental conservation and education, and beekeepers who have experience, working with communities, good communication skills, a knowledge of sustainability, and strong entrepreneurial skills, can use that training and experience in a variety of settings – as agricultural consultants, environmental educators, or researchers. Some others might pursue another advanced degree to transition into teaching or research ecology (entomology or environmental science).


