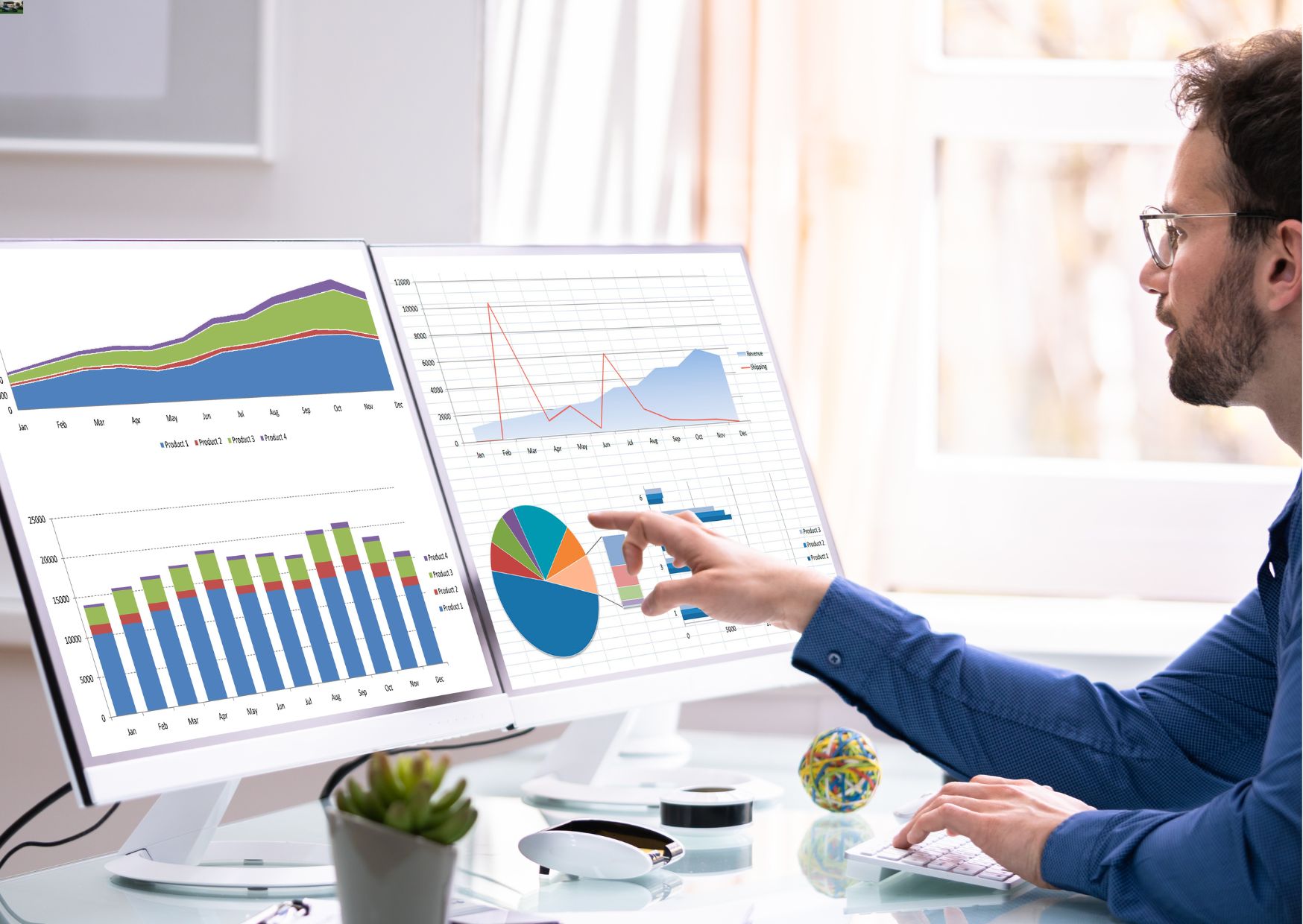
Become a data analyst a career-oriented profession, where your responsibilities are to collect data, process, and perform statistical analysis of information. They are crucial talents for organisations striving to enhance their operations, products, or services through data-driven decisions.

A data analyst collects, cleans, and interprets data sets in order to answer a question or solve a problem.
What are the Main Types of Data Analysts?
The main types of data analysts include Business Data Analysts who enhance operational efficiency, Financial Data Analysts who advise on financial decisions, Marketing Data Analysts who optimize marketing strategies, and Healthcare Data Analysts who improve patient care through data-driven insights.
Business Data Analysts
Business Data Analysts are professionals who use data to analyse and interpret information for businesses. They identify trends and patterns to support strategic decision-making and improve operational efficiency.
Role and Key Responsibilities:
Business data analysts interpret data to enhance efficiency, identify patterns, and inform strategic decision-making.
Financial Data Analysts
Financial Data Analysts analyse financial data to provide insights for investment decisions and financial planning within organisations. They use statistical techniques to interpret complex information and offer expert advice to support business objectives.
Role and Key Responsibilities:
Another category includes financial data analysts. As their name suggests, their primary goal is to analyse financial data, prepare reports, and offer specialist advice to guide investment decisions and financial planning.
Marketing Data Analysts
Marketing Data Analysts analyse data from marketing campaigns, customer behaviour, and market trends to enhance strategies and improve return on investment (ROI) for businesses.
Role and Key Responsibilities:
A marketing data analyst studies data on marketing campaigns, customer behaviour, and market trends to enhance marketing strategies and the return on investment.
Healthcare Data Analysts
Healthcare Data Analysts analyse medical data to improve patient care and operational efficiency within healthcare organisations. They use statistical techniques to identify trends and support decision-making processes.
Role and Key Responsibilities:
Healthcare data analysts work with medical data to find trends, improve patient care, and support management decisions in the healthcare field.
What does a Data Analyst do?

A business analyst leverages data collection, analysis, and visualisation to identify trends, communicate insights effectively to stakeholders, and ensure data accuracy to support informed decision-making within organisations.
Collecting and Cleaning Data
These data analysts collect data from different sources, clean it, and unify it so that it can be compared, sorted, analysed, and merged with other datasets.
Analysing Data to Identify Trends and Patterns
They apply statistical methods and the right set of tools for the analysis of data to identify trends, patterns, and insights from observations made.
Creating Visualisations and Reports
Data analysts use visualisations and reports to effectively communicate their findings, enabling stakeholders to interpret and act upon insights derived from data analysis.
Communicating Findings to Stakeholders
They translate their findings into language that is accessible to stakeholders and convincing to help them make decisions.
Supporting Decision-Making Processes with Data Insights
Data analysts use data-driven insights to inform and improve decision-making processes within organisations, ensuring informed choices and strategic advantages.
Ensuring Data Accuracy and Integrity
Data analysts ensure data accuracy by rigorously verifying its sources, consistency, and security, maintaining reliability for informed decision-making.
Average Salary Range of Data Analyst
Data analysts’ salary ranges widely depending on their experience, location, and industry, reflecting variations across different sectors and geographic regions.
Salary Ranges Based on Experience and Location
The salary for data analysts varies widely based on experience, location, and industry. Entry-level data analysts in the UK earn between £25,000 to £35,000 annually, while in the US, the range is $50,000 to $70,000 per year. With more experience, analysts earn between £35,000 to £50,000 annually in the UK and $70,000 to $90,000 annually in the US. Highly experienced analysts in specialised roles can earn £50,000 to £70,000 or more per year in the UK and $90,000 to $120,000 or more per year in the US.
Comparison of Salaries in Different Industries
Salaries can vary significantly across industries. Sectors such as finance, technology, and medicine typically offer higher salaries compared to retail or non-profit organisations.
Factors That Influencing Data Analyst Salaries
Several factors influence data analyst salaries:
- Experience: Data analysts with more experience tend to earn higher salaries due to their advanced skills and responsibilities.
- Industry: Salary levels can vary widely depending on the sector, with higher-paying industries generally offering higher salaries.
- Location: Salary levels may differ based on the location, with larger urban areas typically offering higher salaries compared to rural or mid-sized areas.
Essential Skills of a Data Analyst
To become a successful Data Analyst, you need to bring together technical and soft skills.
Technical Skills
- Proficiency in Data Analysis Tools: Data analysts must be proficient in using data analysis tools such as Excel, SQL, Python, and R to manipulate and analyze data.
- Knowledge of Statistical Methods and Data Visualization: Understanding statistical methods and being able to create effective data visualizations are crucial for analyzing and presenting data.
Soft Skills
- Analytical Thinking: Data analysts must interpret data and identify trends or patterns as part of their role.
- Communication: Effective communication skills are essential for presenting findings and collaborating with stakeholders.
- Problem-Solving: Problem-solving skills enable data analysts to address data-related challenges and provide actionable insights.
- Attention to Detail: Attention to detail is vital for ensuring data accuracy and integrity.
Career Development Tips for Data Analysts
- Staying Updated with Industry Trends and Tools: Learning about the latest data analysis tools and industry trends is crucial. A data analyst should always be at the forefront of the ever-shifting technology world and be aware of all the latest trends and tools.
- Networking with Professional Organisations and Industry Events: Networking with professional organisations and attending industry events can open doors to career opportunities for marketing graduates.
- Gaining Experience Through Internships and Projects: Internships and projects are recognised ways to gain experience in the data analysis field. They help candidates acquire hands-on experience and build an impressive portfolio.
- Consistently Improving Technical and Analytical Skills: To excel in a data analyst career, continuous improvement and practice of technical and analytical skills are essential.
Qualification and Requirements for Data Analysts
To become a Data Analyst specific educational and professional requirements must be met.
Educational Requirements
- Bachelor’s Degree in Data Science, Computer Science, Statistics, or Related Field: Formal education in a related field is essential; typically, a bachelor’s degree is required for most positions.
- Relevant Coursework in Statistics: Coursework in data analysis, statistics, and programming is crucial for success as a data analyst.
Certification Requirements (If Applicable)
- Professional Certifications: Obtaining certifications such as Certified Analytics Professional (CAP) or Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate can enhance qualifications and demonstrate competency.
- Continuous Professional Development (CPD): Engaging in ongoing CPD activities relevant to data analysis, such as attending workshops, webinars, or conferences, further demonstrates a commitment to professional growth and staying updated with industry trends.
Experience Requirements
- Internships and Entry-Level Positions: Undertaking unpaid or low-paid internships is essential for developing skills and establishing professional credibility.
- Practical Project Experience: Gaining hands-on experience through practical projects, either within academic settings or through freelance work, provides valuable real-world application of theoretical knowledge.
How to Become a Data Analyst
To become a business analyst, earn a relevant bachelor’s degree in fields like data science or statistics. Gain practical experience through internships and freelance projects, while building a strong portfolio showcasing diverse data projects and problem-solving abilities.
Completing Relevant Education
- Obtain a Bachelor’s Degree in a Related Field: Earn a bachelor’s degree in data science, computer science, statistics, or a related field.
- Specialise in Advanced Data Analysis and Programming Courses: Take courses that advance your knowledge and programming skills.
Gaining Practical Experience
- Internships and Entry-Level Data Analyst Roles: Undertake internships and entry-level positions in data analysis to hone your skills and build a portfolio.
- Freelance Projects: Engaging in freelance data analysis projects provides practical experience and allows for the application of skills in real-world scenarios.
Building a Strong Portfolio
- Showcase a Portfolio of Diverse and High-Quality Data Projects: Showcase your competency in data projects through a portfolio that demonstrates a variety of works. This highlights your ability to handle various tasks in data analytics, including data cleaning, visualization, and reporting.
- Case Studies and Problem-Solving Examples: Include detailed case studies or examples of how you have solved specific data-related problems or challenges. This provides concrete evidence of your analytical skills and problem-solving abilities in real-world scenarios.
Networking and Professional Development
- Joining Professional Societies: Join a professional organisation such as the Data Science Society or the Association for Data Science and Analytics to network with peers, learn about best practices, and stay updated on the industry landscape.
- Participating in Industry Events and Workshops: Attend industry events such as conferences and workshops to learn from others, stimulate intellectual growth, and expand your professional network. This also provides opportunities to connect with potential employers or collaborators.
Get Qualified as a Data Analyst
Data Analysis Essentials, Data Entry Essentials, Data Analysis Foundations, Data Entry Diploma
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Why should you be a Data Analyst?
Data analysts enjoy a challenging and influential working life. They work with data to uncover information critical to business operations, influencing decisions in areas such as product lines, purchasing, and marketing. The role offers good job security, excellent earning potential, and numerous opportunities for training and advancement. Most importantly, data analysts contribute to enhancing business performance while tackling crucial problems.
- Is Becoming a Data Analyst a Good Career Choice for You?
Furthermore, if you are passionate about data, possess strong analytical and problem-solving abilities, excel with numbers, enjoy discovering patterns and trends, appreciate statistics and data visualization, and value continuous learning and development, a career as a data analyst can be highly rewarding. This career path offers substantial opportunities for growth and learning, especially if you enjoy deriving insights from data to drive meaningful decisions.
- Average Salary Range of a Data Analyst
Salaries for data analysts vary significantly based on experience, location, and industry. In the UK, entry-level positions typically pay between £25,000 and £35,000 annually, while mid-tier roles can earn between £35,000 and £50,000. Senior data analysts or specialized roles may command salaries starting from £50,000 annually. In the US, salaries range from $50,000 to $70,000 for entry-level positions, with senior roles potentially earning $90,000 to $120,000 or more annually.
- Which Qualifications Can Help with a Career as a Data Analyst?
A bachelor’s degree in data science, computer science, statistics, or a related field is generally required. Additional courses and training in data analysis, programming, and statistical methods enhance employability. Certifications such as Certified Analytics Professional (CAP), Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate, and Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate demonstrate proficiency in data analysis. Internships and entry-level positions provide practical experience and credibility.
- Do I Need to Be Experienced to Get Started?
You don’t necessarily need extensive experience to begin a career as a data analyst. Many professionals start with a foundational education in business intelligence (BI) and gain practical skills through internships or early jobs focused on data analysis. A willingness to learn and a passion for working with data are key attributes for success in this field.
- Data Analyst Career Outlook
The outlook for data analysts is promising across various industries such as financial services, manufacturing, healthcare, technology, and marketing. Data analysis is essential for businesses to enhance competitiveness, ensuring strong job security and opportunities for advancement into specialist or managerial roles.
- Data Analyst Hierarchy and Progressing Within the Role
Entry-level positions include junior data analyst or data analyst roles. Mid-level positions encompass senior data analyst or data scientist roles. Advanced roles may include positions such as data engineering manager, analytics manager, or chief data officer. Career advancement typically requires continuing education, advanced certifications, and ongoing skill development.
- Data Analyst Exit Options and Opportunities
As we can see, Data Analysts have numerous exit options and opportunities. Their technical skills provide them with the expertise to pursue various professional paths that involve data analysis or explore derived insights. Beginning their careers as Data Analysts serves as a solid foundation, from which they may transition into different roles such as data scientist, business intelligence analyst, or consultant. They can accumulate valuable experience over the years or choose to pursue advanced degrees in academia. Ultimately, they may also find employment as data educators or researchers.